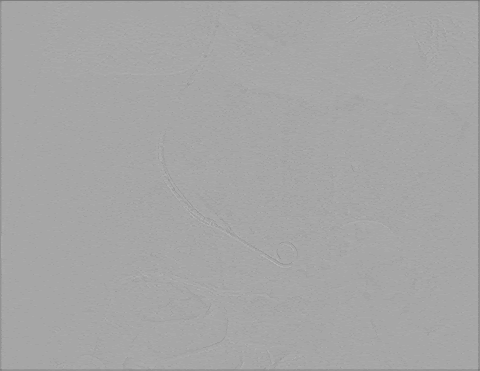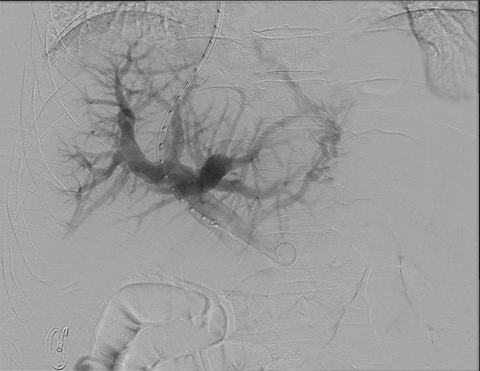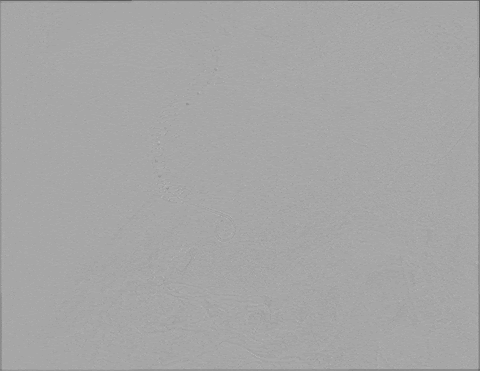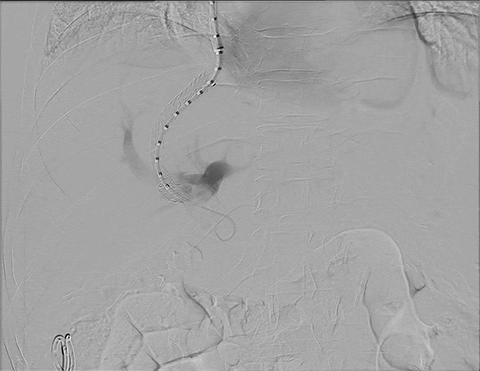Interventional radiologists are often members of the palliative care team involved in the treatment of cancer patients who are entering the last phase of an illness that cannot be treated. An interventional radiologist can help provide symptom management and treatments for pain relief when decided upon by a patient and their care team.
- Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty: Image guided cement mixture injection into a fractured vertebral body for relieving spinal pain and increasing mobility
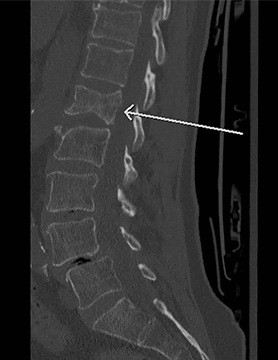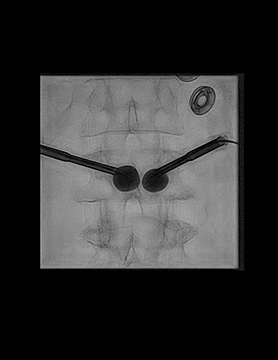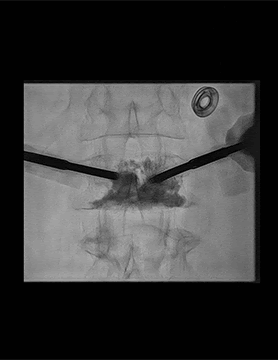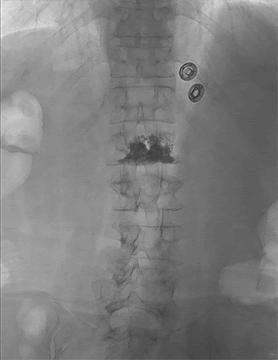
- Nerve blocks: Several nerve roots (celiac plexus, hypogastric, intercostal, transverse abdominal plane) in the body can be ablated or blocked to help reduce patient’s pain and reduce the need for narcotics
- Thoracentesis is the removal of fluid that has accumulated in the chest around the lung. Drainage is typically performed through a small hollow needle which is inserted under ultrasound guidance.
- Paracentesis is the removal of fluid that has accumulated in the abdomen or pelvis. Drainage is typically performed through a small hollow needle which is inserted under ultrasound guidance.
- PleurX drainage catheters are hollow tubes that can be placed into the chest or abdominal cavity to allow for drainage of recurrent fluid collections. These catheters are typically placed using xray and ultrasound guidance and can be kept in place for extended periods of time
- Epidural steroid injections (ESI) – Medicines are injected into the epidural space; a fat-filled area between the bone and the protective sac of the spinal nerves to help relieve neck, arm, back, and leg pain caused by inflamed spinal nerves due to spinal stenosis or disc herniation. Pain relief may last for several days or even years. The procedure is performed under x-ray guidance on an outpatient basis.
- Feeding support tube is a small catheter that is safely inserted directly into the stomach for people who are unable to take in sufficient food by mouth. Often referred to as a feeding tube, gastrostomy tube or G-tube.
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a technique used to reduce internal bleeding in the stomach and esophagus, or to decrease the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites) in patients with cirrhosis by creating a shunt to bypass a diseased or cirrhotic liver. Utilizing x-ray guidance a stent (a tiny mesh tube) is placed to create a channel allowing blood draining from the bowel to bypass the liver and return to the heart.